This information was adapted from the National Eye Institute to help patients and their families search for general information.
Glaucoma Eye Chart
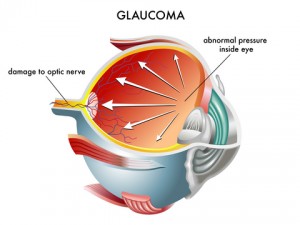
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that can damage the eye’s optic nerve and result in vision loss and blindness. Glaucoma occurs when the normal fluid pressure inside the eyes slowly rises. However, with early treatment, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss.
The optic nerve is a bundle of more than 1 million nerve fibers. It connects the retina to the brain. (See diagram below.) The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. A healthy optic nerve is necessary for good vision.
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form. Some people have other types of this disease.
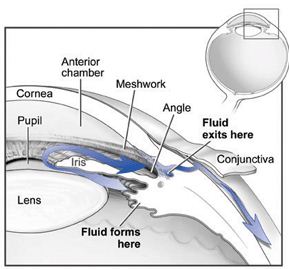
In the front of the eye is a space called the anterior chamber. A clear fluid flows continuously in and out of the chamber and nourishes nearby tissues. The fluid leaves the chamber at the open angle where the cornea and iris meet. (See diagram below.) When the fluid reaches the angle, it flows through a spongy meshwork, like a drain, and leaves the eye.
Sometimes, when the fluid reaches the angle, it passes too slowly through the meshwork drain. As the fluid builds up, the pressure inside the eye rises to a level that may damage the optic nerve. When the optic nerve is damaged from increased pressure, open-angle glaucoma–and vision loss–may result. That’s why controlling pressure inside the eye is important.
Anyone can develop glaucoma. Some people are at higher risk than others. They include:
A comprehensive dilated eye exam can reveal more risk factors, such as high eye pressure, the thinness of the cornea, and abnormal optic nerve anatomy. In some people with certain combinations of these high-risk factors, medicines in the form of eye drops reduce the risk of developing glaucoma by about half.
Medicare covers an annual comprehensive dilated eye exam for some people at high risk for glaucoma.
Studies have shown that the early detection and treatment of glaucoma before it causes major vision loss, is the best way to control the disease. So, if you fall into one of the high-risk groups for the disease, make sure to have your eyes examined through dilated pupils every two years by an eye care professional.
If you are being treated for glaucoma, be sure to take your glaucoma medicine every day. See your eye care professional regularly.
At first, there are no symptoms. Vision stays normal, and there is no pain.
However, as the disease progresses, a person with glaucoma may notice his or her side vision gradually failing. That is, objects in front may still be seen clearly, but objects to the side may be missed.
As glaucoma remains untreated, people may miss objects to the side and out of the corner of their eye. Without treatment, people with glaucoma will slowly lose their peripheral (side) vision. They seem to be looking through a tunnel. Over time, straight-ahead vision may decrease until no vision remains.
Glaucoma can develop in one or both eyes.

Normal Vision

Same scene viewed by a person with glaucoma
Glaucoma is detected through a comprehensive eye exam that includes:
Yes. Immediate treatment for early-stage, open-angle glaucoma can delay the progression of the disease. That’s why early diagnosis is very important.
Glaucoma treatments include medicines, laser trabeculoplasty, conventional surgery, or a combination of any of these. While these treatments may save remaining vision, they do not improve sight already lost from glaucoma.

As with laser surgery, conventional surgery is performed on one eye at a time. Usually, the operations are four to six weeks apart. Conventional surgery is about 60 to 80 percent effective at lowering eye pressure. If the new drainage opening narrows, a second operation may be needed. Conventional surgery works best if you have not had previous eye surgery, such as a cataract operation.
In some instances, your vision may not be as good as it was before conventional surgery. Conventional surgery can cause side effects, including cataracts, problems with the cornea, and inflammation or infection inside the eye. The buildup of fluid in the back of the eye may cause some patients to see shadows in their vision. If you have any of these problems, tell your doctor so a treatment plan can be developed.
Conventional surgery makes a new opening for the fluid to leave the eye.
If eye drops have been prescribed for treating your glaucoma, you need to use them properly and as instructed by your eye care professional. Proper use of your glaucoma medication can improve the medicine’s effectiveness and reduce your risk of side effects.